Understanding the Autonomic Nervous System: A Guide to Your Body's Inner Workings
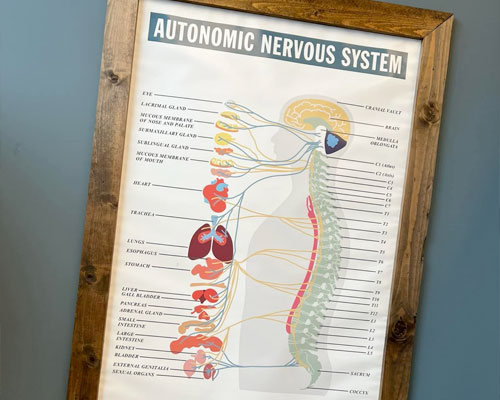
In the waiting area of Camarata Chiropractic in Rochester, NY, hangs an intriguing chart titled "Autonomic Nervous System." This chart is more than just wall decor; it offers a profound insight into the complex and vital system that controls the involuntary functions of our body. Let's dive deep and understand its significance.
The Autonomic Nervous System: An Overview
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a part of the peripheral nervous system responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions, such as heartbeat, blood flow, digestion, and respiratory rate. It acts as a control system, functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and ensures that the body responds correctly to changing environments.
Key Components and Their Roles
Brain
The central hub of the entire nervous system, the brain, plays a pivotal role in processing information received from the nerves throughout the body. The brain ensures that the body responds appropriately, whether it's speeding up the heartbeat during stressful situations or regulating digestion after a meal.
Eyes and Glands
The eyes, being our primary sensory organs, relay visual data to the brain. Adjacent to the eyes are the lacrimal glands responsible for producing tears, and the mucous membrane of the nose, which moistens the inhaled air. There's also the sublingual gland beneath the tongue, producing saliva, which aids in the early stages of digestion.
Heart, Trachea, Lungs, and Esophagus
The heart, trachea, lungs, and esophagus work in tandem to ensure oxygen-rich blood circulation and respiration. The heart pumps blood throughout the body, the trachea serves as an air conduit to the lungs, and the lungs oxygenate the blood. The esophagus, on the other hand, connects the throat to the stomach, transporting food for digestion.
Digestive and Excretory Organs
The liver, gallbladder, and stomach play vital roles in digestion and detoxification. The liver processes nutrients, produces bile, and detoxifies harmful substances. The gallbladder stores bile, which breaks down fats, while the stomach digests food. Kidneys eliminate waste from the body, and the bladder stores urine until it is excreted.
Reproductive Organs
The chart also touches on the autonomic nervous system's role in regulating reproductive organs, highlighting the intricate balance the ANS maintains for the body's overall function.
Spinal Cord: The Communication Highway
Running down from the brain, the spinal cord acts as a communication highway, with nerves branching out to every part of the body. It is categorized into sections - cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, and coccyx - each connecting to specific parts of the body.
Why is This Significant at Camarata Chiropractic?
In Western NY, particularly in North Chili, NY, understanding the autonomic nervous system is crucial when considering chiropractic care. Misalignments in the spine can impede the nervous system's function, leading to various health issues. By ensuring the spine is properly aligned, chiropractic care aids in ensuring the ANS functions optimally, maintaining overall health and wellness.
In Conclusion
The autonomic nervous system is a testament to the body's wonder, with its intricate web of connections and reflexes keeping us alive and functioning every day. By understanding its workings, we appreciate the importance of regular chiropractic check-ups to ensure our body remains in harmony. If you're in the Rochester or North Chili, NY area, consider reaching out to Camarata Chiropractic to discuss how chiropractic care can benefit your autonomic nervous system and overall health.
